
This happens because people differ in how they metabolize the medications.

Some people experience grogginess in the morning even with sleep medications from this newer class. They're called "non-benzodiazepines", a confusing name given that they still operate by acting on the benzodiazepine receptors. Therefore, these newer sleep medications are safer and have lower potential for dependence and fewer side effects. Most of these newer medications work on the benzodiazepine receptors in the brain, but do it more selectively than the medications in the benzodiazepine class. In addition, some medications in this class can produce a "hangover" or grogginess the next day.įor these reasons, newer sleep medications have been developed and approved by the FDA. Benzodiazepines are generally recommended for short-term use because tolerance and dependence can develop. Other benzodiazepine medications approved by the FDA for the treatment of anxiety, such as Lorazepam, Clonazepam, and Alprazolam, are sometimes prescribed for insomnia as well. The following five medications, listed in alphabetical order, are approved by the FDA for the treatment of insomnia: These medications are older and have a higher potential for dependency. One class of sleep medication is called benzodiazepines. The discussion is organized by classes of medication. Below is a brief discussion of medications that are commonly used for sleep. These are called hypnotic medications or sleep medications. What is depression? A Mayo Clinic expert explains.The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved certain medications for the treatment of insomnia.Depression and anxiety: Can I have both?.CPAP machines: Tips for avoiding 10 common problems.Clinical depression: What does that mean?.Antidepressants: Which cause the fewest sexual side effects?.Antidepressants: Selecting one that's right for you.Antidepressants: Can they stop working?.Antidepressants and weight gain: What causes it?.Antidepressants and alcohol: What's the concern?.Antidepressant withdrawal: Is there such a thing?.
TREATING SEVERE INSOMNIA PROFESSIONAL
Depending on the cause of insomnia, a referral to a mental health professional may help some people.

Your doctor may prescribe medication and have you try other strategies to get your sleep pattern back on track. To determine the cause and best treatment for insomnia, you may need to see a sleep specialist. If you keep having sleep problems, talk to your doctor. Also, treating insomnia may help depression symptoms improve faster. Treatment for one of these underlying conditions may be necessary for insomnia to get better. In some cases, insomnia is caused by a medical condition such as sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome or chronic pain, or by a mental health disorder such as depression. Go to another room and read or do other quiet activities until you feel sleepy.

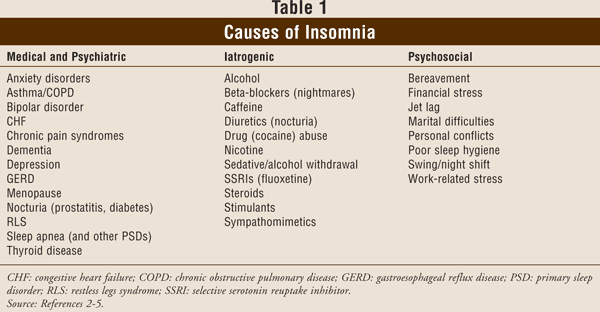
In addition to smoking being a major health risk, nicotine use can interfere with sleep. Both caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
